How to Create a LinkedList in Java
LinkedList is also a linear data structure like ArrayList, but it doesn’t store elements in contiguous locations like ArrayList. Elements in LinkedList are connected with each other using pointers. Each element in LinkedList has a pointer to the next element.
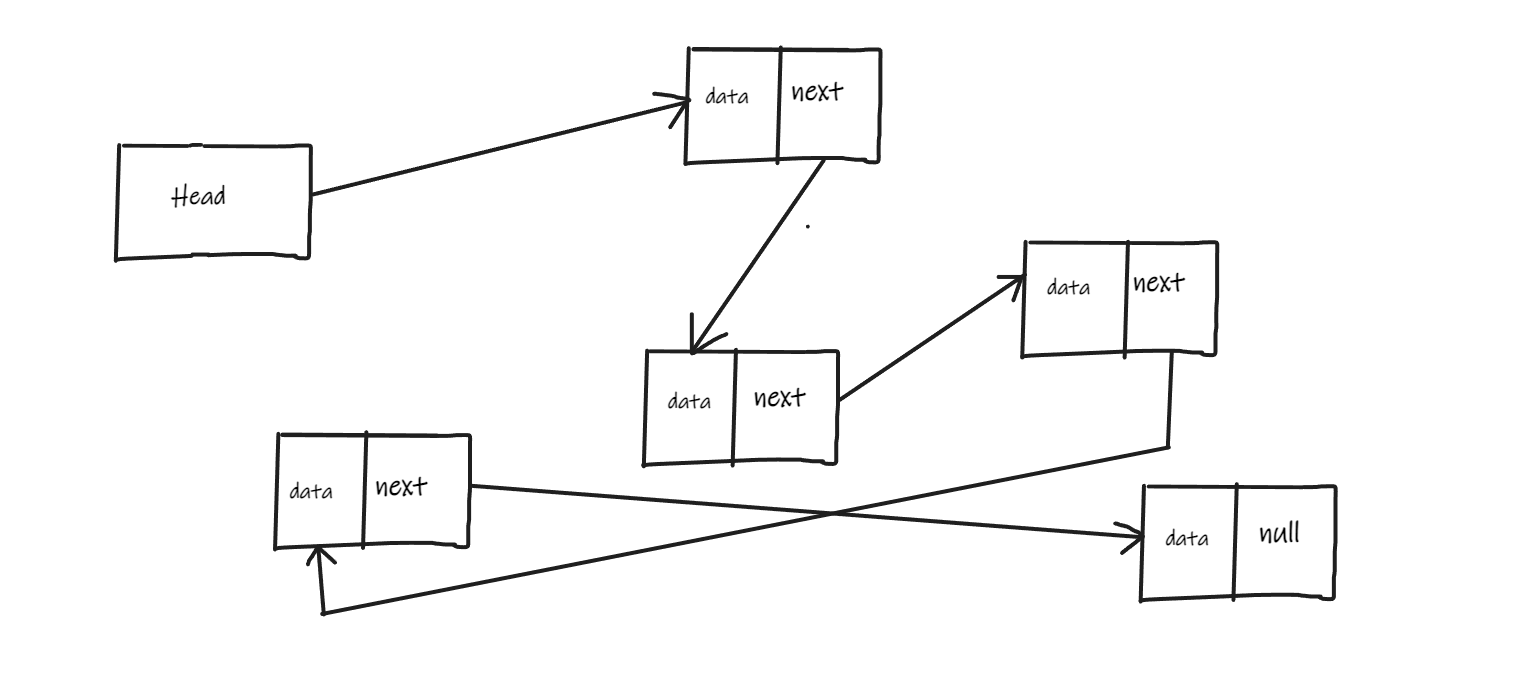
So, what is the difference between a LinkedList and an ArrayList.
LinkedList Class Declaration
public class LinkedList extends AbstractSequentialList implements List, Deque, Cloneable, java.io.SerializableDifference between ArrayList and LinkedList
| ArrayList | LinkedList |
|---|---|
| Is a linear data structure that stores elements in contiguous locations | Linear data structure that stores elements using links to each other |
| Uses arrays dynamically | Uses doubly linked list |
| Addition, removal of elements is slower as compared to LinkedList because it requires shifting of all the elements if one element is added or removed from the array list | It is faster as it only requires updating links to the next element in the linked list. |
| Best suited for storing and accessing data | Best suited if our list requires manipulation of data more frequently |
| It works purely as a list | It can work as a list as well as a queue, since it implements List and Queue interfaces |
How to create a LinkedList
List<String> list = new LinkedList<String>();
LinkedList<String> linkedList = new LinkedList<String>();The above statement will create a linked list which can store String type objects.
package com.javatrainingschool;
import java.util.*;
public class LinkedListExample {
public static void main(String [] args) {
List<String> linkedList = new LinkedList<String>();
linkedList.add("Sachin");
linkedList.add("Saurav");
linkedList.add("Rahul");
//iterate over this list using iterator
Iterator<String> it = linkedList.iterator();
while(it.hasNext()) {
System.out.println("Element : " + it.next());
}
}
}Output :
Element : Sachin
Element : Saurav
Element : RahulWhich is better between LinkedList and ArrayList
Both have their own utility in difference scenarios. Let’s see which is better in which situation.
- In case of randomly accessing elements, arraylist is faster, because it has reference to every element in the list. Whereas, in case of, LinkedList, we have to traverse from the beginning to the nth element.
- LinkedList are faster in case of deletion of elements, because, in case of arraylist, shifting of elements is required to fill the slot opened by deletion of an element.
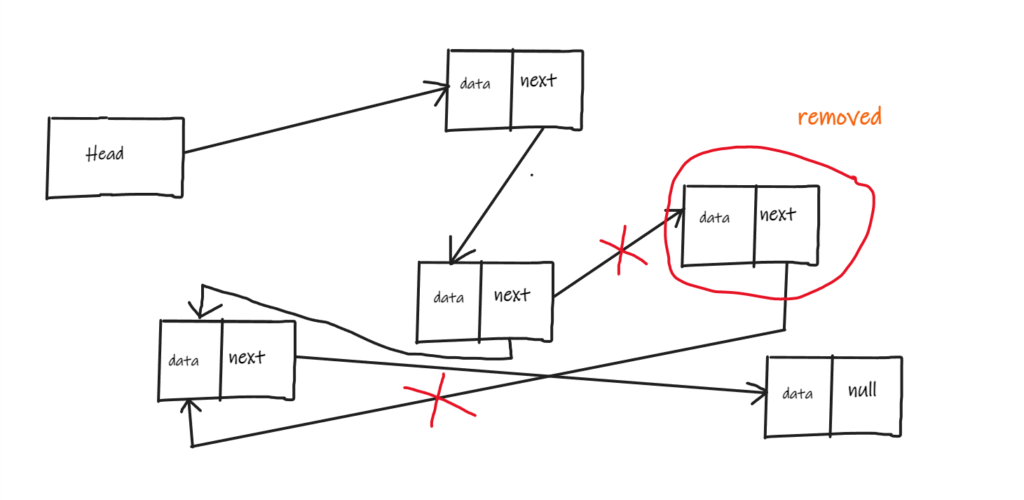
Data removal only needs updating the links in LinkedList. Refer the below diagram
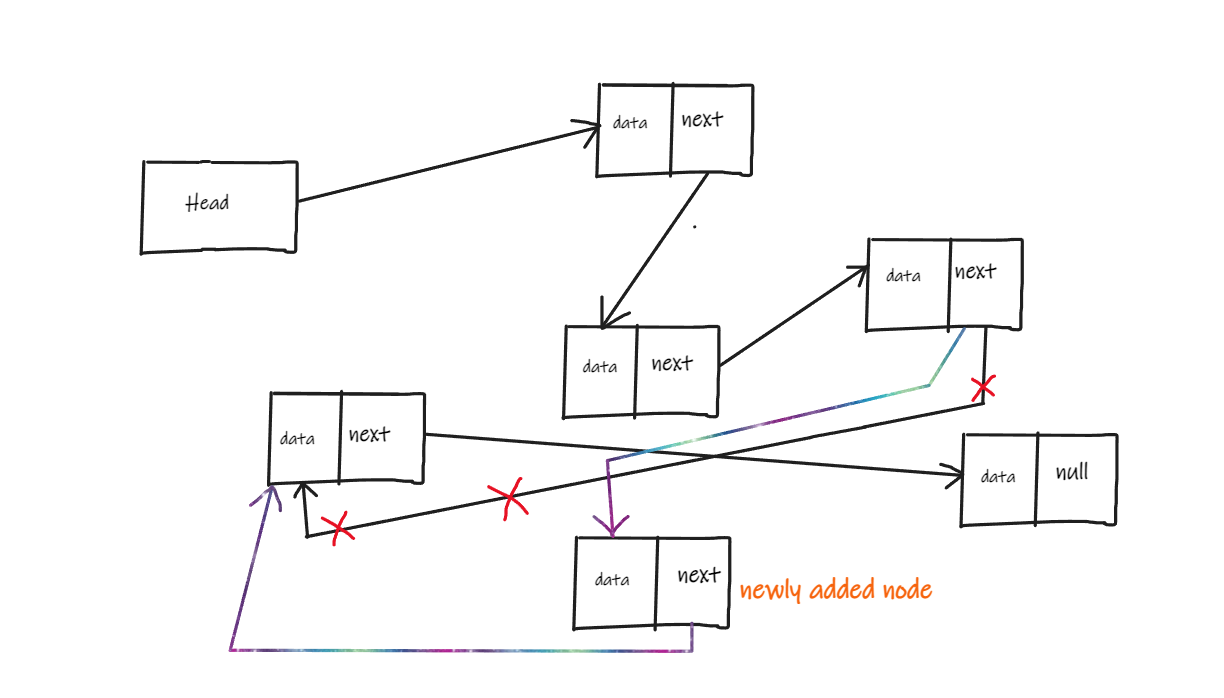
Insertion also needs updating the links in LinkedList. Refer the below diagram
Performance comparision between LinkedList and ArrayList
| Operation | Time Complexity of ArrayList | Time Complexity of LinkedList | Which is Better? |
|---|---|---|---|
| Insertion at a particular index | O(N) | O(N) | LinkedList |
| Get an element by index value | O(1) | O(N) | ArrayList |
| Search by value | O(N) | O(N) | ArrayList |
| Remove by index | O(N) | O(N) | LinkedList |
| Remove by value | O(N) | O(N) | LinkedList |
addFirst and addLast methods in LinkedList
package com.javatrainingschool;
import java.util.LinkedList;
public class LinkedListExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
LinkedList<String> linkedList = new LinkedList<String>();
linkedList.add("Kabir");
linkedList.add("Meera");
linkedList.add("Raskhan");
//this will add Ravidas as the first element in the list
linkedList.addFirst("Ravidas");
//this will add Tulsidas as the last element in the list
linkedList.addLast("Tulsidas");
System.out.println(linkedList);
}
}Output :
[Ravidas, Kabir, Meera, Raskhan, Tulsidas]Removal methods of LinkedList
There are many methods which removes elements from linked list. Let’s see them
linkedList.removeFirst();
linkedList.removeFirstOccurrence("Ravidas");
linkedList.removeLast();
linkedList.removeLastOccurrence("Tulsidas");Descending Iterator of LinkedList
Descending iterator of LinkedList is used to traverse the elements in reverse order.
package com.javatrainingschool;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.LinkedList;
public class LinkedListExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
LinkedList<String> linkedList = new LinkedList<String>();
linkedList.add("Kabir");
linkedList.add("Meera");
linkedList.add("Raskhan");
Iterator it = linkedList.descendingIterator();
while(it.hasNext()) {
System.out.println("Element is : " + it.next());
}
}
}Output :
Element is : Raskhan
Element is : Meera
Element is : Kabir