SOAP Building Blocks
The below picture shows various building blocks of a soap message
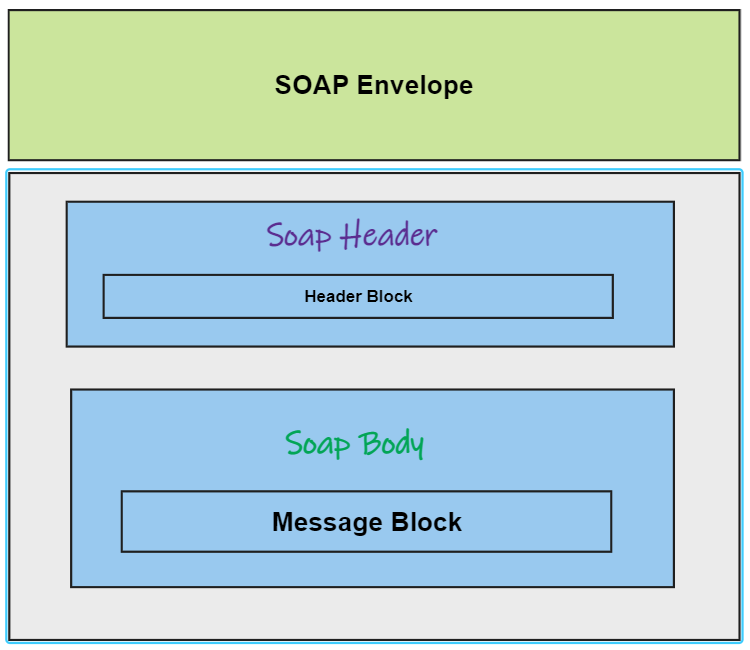
A soap message is a xml document with below blocks.
- SOAP Envelope – An Envelope element identifies the XML document as a SOAP message – This is the root element of the SOAP message. It is used to encapsulate all the details in the SOAP message.
- Header – A Header element contains header information such as authentication credentials. It can also contain the definition of complex types which could be used in the SOAP message.
- Body – A Body element contains data request and response information. Body contains the actual data which needs to be sent between the web service and the client application.
Note -> By default, the SOAP message contains parameters which are simple types such as strings and numbers. But they can also contain complex object type.
SOAP Body example
<soap:Body>
<BookInfo>
<BookName>SOAP Web Services</BookName>
<BookDescription>Learn SOAP based web services</BookDescription>
<Price>1000</Price>
</BookInfo>
</soap:Body>Complete SOAP message structure
Below is an example of a soap request.
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<soap:Envelope xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance">
<soap:Header>
<m:Trans xmlns:m="https://www.javatrainingschool.com/txn/" soap:mustUnderstand="1">
12345
</m:Trans>
</soap:Header>
<soap:Body>
<LibraryWebService xmlns="https://www.javatrainingschool.com/library">
<BookId>100</BookId>
</LibraryWebService>
</soap:Body>
</soap:Envelope>In the above example, we can see that the message contains following three things.
- Envelope
- Header
- Body
Name of the web service in the above example is LibraryWebService. And it takes one parameter called BookId. Value of which in this example is 100.
Note the below points about Envelope element:
- Every soap message must have Envelope as the root element
- Every Envelope must contain one body element
- Header element is optional for Envelope. If it contains a header element, there must be just one. Header must appear as the first child of the Envelope, before the body element.
- The Envelope changes when the SOAP version change
- A v1.2-compliant SOAP processor generates a “Version Mismatch” fault, if the received message does not contain the v1.2 envelope namespace.
SOAP Fault Message
- The SOAP Fault element is used for error messages.
- It is optional.
- The SOAP Fault element holds information about errors and status of a SOAP message.
- Fault element appears as a child element of the Body element. It can appear only once.
Below are the sub elements of SOAP Fault element :
| Fault Sub element | Description |
|---|---|
| <faultcode> | A code for the fault |
| <faultstring> | A meaningful information about the fault |
| <faultactor> | Information about who caused the error |
| <detail> | Has error information related to the body element |
SOAP Fault Code
The fault code values defined below must be used in faultcode element
| Error | Description |
|---|---|
| VersionMismatch | An invalid namespace for the SOAP Envelope element |
| MustUnderstand | An immediate child element of the Header element, with the mustUnderstand attribute set to “1”, was not understood |
| Client | The message was incorrectly formed or contained incorrect information |
| Server | There was a problem with the server so the message could not proceed |