JDBC Prepared Statement
The JDBC API provides Statement object to execute queries, updates, and DDL statements on data in a database. The PreparedStatement is subclass of` Statement that provides better security, portability across vendors, and performance.
SQL command used in a PreparedStatement is pre-compiled or prepared initially and then reused.
PreparedStatement is precompiled
What does pre-compile mean? When we run an SQL command on the database, the database will first validate, parse, and build an execution plan to run it. These steps fall under pre-compiling stage.
When the JDBC driver creates a prepared statement, it asks the database to pre-compile that SQL command. Then, the database will store the pre-compiled command in a cache for the current database connection. If the same SQL command is to be run multiple times, using the pre-compiled version is better for performance since the compilation part has to be done only once.
The database has a limited cache for pre-compiled SQL commands and hence, we cannot have too many of them. Defining parameters helps make the command reusable and therefore reduces the number of distinct commands.
Let’s see one example. We will insert some records here using PreparedStatement
package core_java_project;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.DriverManager;
import java.sql.PreparedStatement;
import java.sql.SQLException;
public class PreparedStatementExample {
public static void main(String[] args) throws ClassNotFoundException, SQLException {
//Loading the driver
Class.forName("com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver");
Connection con = null;
// Step 2 : Getting Connection Object
con = DriverManager.getConnection("jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/test_db", "root", "abcd");
PreparedStatement stmt = con.prepareStatement("insert into doctor values(?,?,?)");
stmt.setInt(1, 102);
stmt.setString(2, "Cardiology");
stmt.setString(3, "Dr Rahul");
stmt.execute();
stmt.setInt(1, 103);
stmt.setString(2, "Dermatology");
stmt.setString(3, "Dr Venkat");
stmt.execute();
System.out.println("Data inserted successfully.");
}
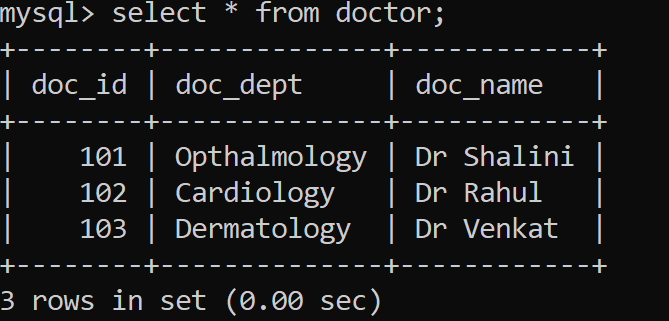
}Output:
Data inserted successfully.In the database
Difference between Statement and PreparedStatement
| Feature | Statement | PreparedStatement |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | It is used to run static queries | It is used to run precompiled queries |
| Query Compilation | Compiled each time the query is executed | Compiled once and can be executed multiple times with different parameters |
| Performance | Less efficient for repeated queries | More efficient for repeated queries due to pre-compilation |
| Reusability | Less reusable for different inputs | Highly reusable with different parameter values |
| Use Case | Suitable for simple and ad-hoc queries | Suitable for complex queries and batch processing. |
| Error Handling | Errors in syntax are detected at run time | Errors in syntax are detected at compile time |
| SQL Injection | More prone to sql injection attacks | Less prone due to parameter binding |