Vector in Java
Vector is a legacy class that works as a dynamic array. It was there in Java before collections framework was introduced in 1.2 version. Later, with introduction of collections framework, ArrayList took place of vector as far as non-multithreaded applications are concerned. But vector is still useful in multithreaded environments.
Important points about vector
- Vector is a legacy class
- It was made part of collections framework in java 1.2
- Vector are dynamic arrays just like ArrayList
- Vector are synchronized unlike ArrayList. Vector are thread-safe and can be used in a multithreaded application.
- In non-multithreaded application, ArrayList would be a better choice.
- Iterators returned by Vector are fail-fast. Which means if you change vector in structure, it will fail and throw ConcurrentModificationException
Class Declaration
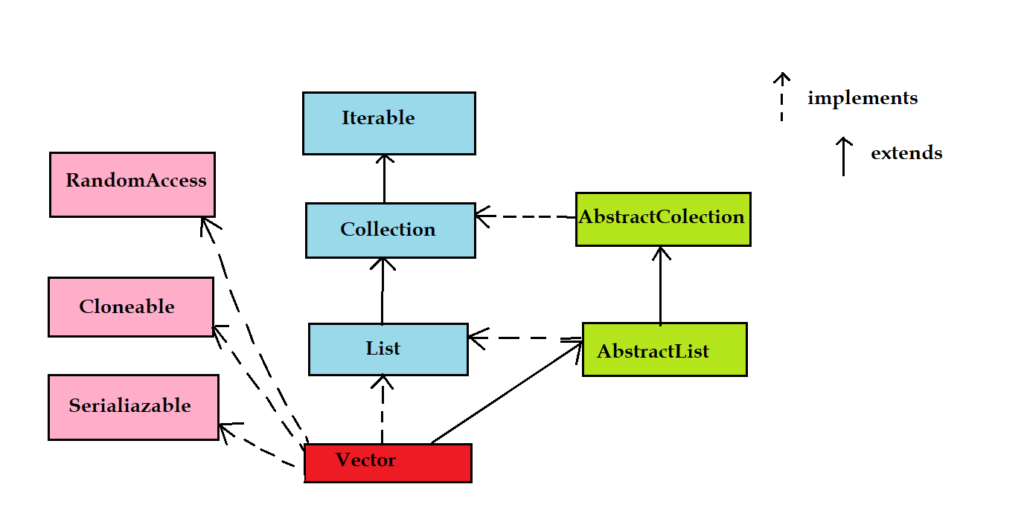
public class Vector extends Object implements List, Cloneable, Serializable
Class Hierarchy
Constructors summary
| Constructor | Description |
|---|---|
| Vector() | Constructs empty vector with initial capacity of 10. |
| Vector(int initialCapacity) | Constructs an empty vector with the specified initial capacity. |
| Vector(int initialCapacity, int capacityIncrement) | It constructs an empty vector with the specified initial capacity and capacityIncrement value. |
| Vector( Collection<? extends E> c) | Constructs a vector that contains the elements of a collection c. |
Vector Example
package com.javatrainingschool;
import java.util.Vector;
public class VectorExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Vector<Integer> vector = new Vector<>();
vector.addElement(10);
//We can also use add method of Collection interface
vector.add(20);
vector.addElement(20);
vector.addElement(30);
vector.addElement(40);
System.out.println("Size of the vector = " + vector.size());
System.out.println("Index of number 30 = " + vector.indexOf(30));
System.out.println("First element of the vector = " + vector.firstElement());
System.out.println("Last element of the vector = " + vector.lastElement());
}
}
Output :
Size of the vector = 5
Index of number 30 = 3
First element of the vector = 10
Last element of the vector = 40
Iterate Vector using Enumeration
package com.javatrainingschool;
import java.util.Enumeration;
import java.util.Vector;
public class VectorExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Vector<Integer> vector = new Vector<>();
vector.addElement(10);
//We can also use add method of Collection interface
vector.add(20);
vector.addElement(20);
vector.addElement(30);
vector.addElement(40);
Enumeration<Integer> en = vector.elements();
while(en.hasMoreElements()) {
System.out.println("Element = " + en.nextElement());
}
}
}
Iterate Vector using enhanced for loop
package com.javatrainingschool;
import java.util.Vector;
public class VectorExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Vector<Integer> vector = new Vector<>();
vector.addElement(10);
// We can also use add method of Collection interface
vector.add(20);
vector.addElement(20);
vector.addElement(30);
vector.addElement(40);
for (int number : vector) {
System.out.println("Element = " + number);
}
}
}Iterate vector using iterator
package com.javatrainingschool;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.Vector;
public class VectorExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Vector<Integer> vector = new Vector<>();
vector.addElement(10);
// We can also use add method of Collection interface
vector.add(20);
vector.addElement(20);
vector.addElement(30);
vector.addElement(40);
Iterator<Integer> it = vector.iterator();
while(it.hasNext()) {
System.out.println("Element = " + it.next());
}
}
}Output :
Element = 10
Element = 20
Element = 20
Element = 30
Element = 40